
Foreman è un software open source per la gestione delle macchine client e server.
Tramite Foreman è possibile effettuare il provisoning su bare metal o sui principali virtualizzatori, oltre che effettuare il monitoraggio delle risorse fisiche e virtuali.
È possibile estendere le funzionalità di Foreman tramite plugins e smart proxies.
I plugins vengono installati sul server di Foreman; esiste ad esempio un plugin per connettere Foreman a PuppetDB.
Gli smart proxies sono macchine fisiche o virtuali in cui viene installato un apposito servizio che comunica con Foreman.
Foreman, tramite lo smart proxy, è in grado di gestire alcuni servizi della macchina in cui è installato.
Lo smart proxy è integrabile con i principali software di gestione delle macchine (come Puppet, Ansible e Salt) e con altri servizi come TFTP, realm AD…
Le connessioni tra Foreman e i suoi smart proxy sono bidirezionali, perciò è necessario abilitare i flussi sul firewall in entrambe le direzioni.
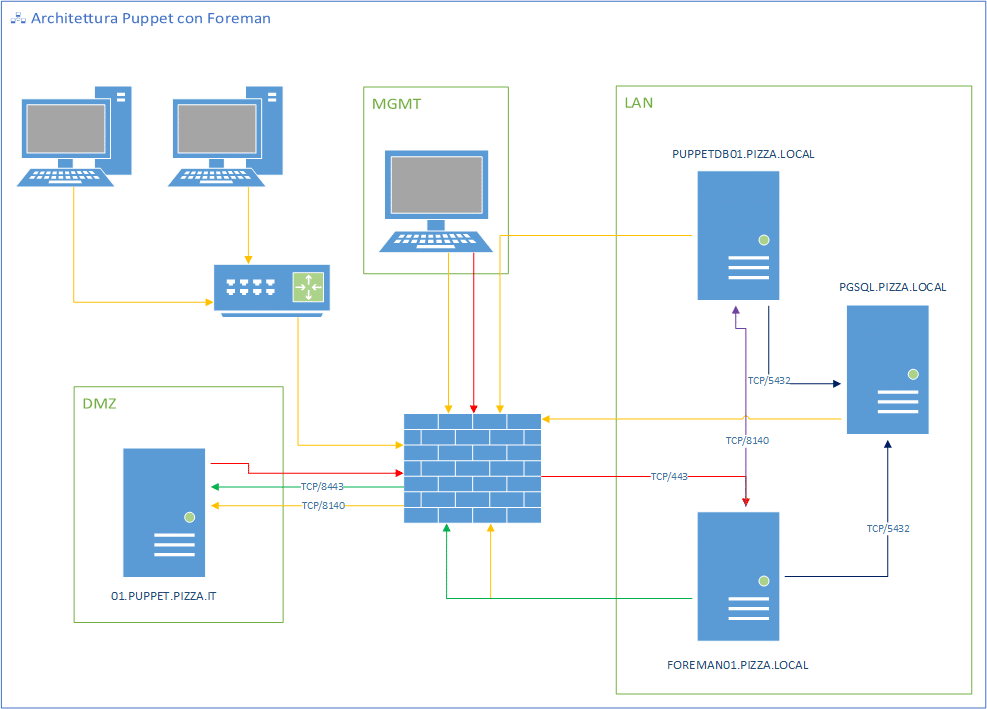
ARCHITETTURA
Per l’installazione di Foreman verrà utilizzato un container LXC con Debian 11.
Sul Puppet master verrà installato e configurato lo smart proxy per Puppet e Puppet CA.
Come database di Foreman verrà utilizzata la stessa istanza di PostgreSQL che è stata utilizzata per PuppetDB.
Si sconsiglia di esporre Foreman su internet, essendo esso un servizio con il quale è facilmente possibile ottenere l’accesso remoto alle macchine.
PORTE UTILIZZATE
foreman01.pizza.local
: TCP/443 HTTPS Foreman
01.puppet.pizza.it: TCP/8140 HTTPS Puppet server e TCP/8443 HTTPS Foreman smart proxy
puppetdb01.pizza.local: TCP/8140 HTTPS PuppetDB
pgsql.pizza.local: TCP/5432 PostgreSQL
FLUSSI DA ABILITARE
foreman01.pizza.local -> 01.puppet.pizza.it: TCP/8140, TCP/8443
foreman01.pizza.local -> puppetdb01.pizza.it: TCP/8140
foreman01.pizza.local -> pgsql.pizza.local: TCP/5432
01.puppet.pizza.it -> foreman01.pizza.local: TCP/443
01.puppet.pizza.it -> puppetdb01.pizza.local: TCP/8140
puppetdb01.pizza.local -> 01.puppet.pizza.it: TCP/8140
puppetdb01.pizza.local -> pgsql.pizza.local: TCP/5432
pgsql.pizza.local -> 01.puppet.pizza.it: TCP/8140
PREREQUISITI
Si suppone che si abbia già installato e configurato Puppet server e PuppetDB seguendo la guida seguente
Se si fosse installato Puppet e i relativi servizi senza consultare la guida, si consiglia di prenderne visione, per avere una maggiore comprensione dell’architettura.
INSTALLAZIONE
Sull’host foreman01.pizza.local aggiornare il sistema operativo con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 2 |
apt update apt upgrade -y apt autoremove -y |
Aggiungere nel file hosts (in alternativa è possibile usare il DNS):
|
0 |
<ip_puppetserver> puppet.pizza.it ca.puppet.pizza.it |
INSTALLAZIONE DI PUPPET AGENT
Aggiungere le repository di Puppet con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
cd /dev/shm wget https://apt.puppet.com/puppet7-release-bullseye.deb dpkg -i puppet7-release-bullseye.deb apt update |
Installare il pacchetto Puppet Agent con il comando:
|
0 |
apt install puppet-agent |
Aggiungere nel file /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf il seguente output:
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
[main] certname = foreman01.pizza.local server = puppet.pizza.it ca_server = ca.puppet.pizza.it dns_alt_names = foreman.pizza.local runinterval = 30m /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent -t |
A questo punto sarà necessario firmare il certificato dell’agent sulla CA di Puppet con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 |
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca list --all /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca sign --cert foreman01.pizza.local |
Successivamente, eseguire l’agent su foreman01.pizza.local con il comando:
|
0 |
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent -t |
INSTALLAZIONE DI FOREMAN
Aggiungere i repository di Foreman con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
wget https://deb.theforeman.org/foreman.asc -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/foreman.asc echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ bullseye 3.5" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ plugins 3.5" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list apt update |
Sull’host pgsql.pizza.local eseguire i comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
apt install sudo sudo -u postgres psql CREATE USER foreman ENCRYPTED PASSWORD '<foreman_db_password>'; CREATE DATABASE foreman WITH OWNER = foreman; |
Sull’host 01.puppet.pizza.it eseguire il comando:
|
0 |
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet module install theforeman-foreman --version 23.1.0 |
Creare il file /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/manifests/foreman01.pizza.local.epp ed inserire il seguente output:
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
# # From: https://github.com/theforeman/puppet-foreman/blob/master/manifests/init.pp # node 'foreman01.pizza.local' { # Here we install and configure Foreman class { 'foreman': initial_admin_username => 'admin', initial_admin_password => '<admin_password>', initial_admin_first_name => '<admin_firstname>', initial_admin_last_name => '<admin_lastname>', initial_admin_email => '<admin_email>', db_manage => false, foreman_url => 'https://foreman.pizza.local', apache => true, servername => 'foreman01.pizza.local', serveraliases => ['foreman.pizza.local'], ssl => true, db_host => 'pgsqlvip.pizza.local', db_port => 5432, db_database => 'foreman', db_username => 'foreman', db_password => '<foreman_db_password', db_sslmode => 'require', db_root_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', server_port => 80, server_ssl_port => 443, server_ssl_ca => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', server_ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', server_ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', server_ssl_crl => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/crl.pem', server_ssl_protocol => 'all -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1', client_ssl_ca => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', client_ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', client_ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', oauth_active => true, oauth_map_users => false, oauth_consumer_key => '<oauth_random_string>', oauth_consumer_secret => '<oauth_longer_random_string>', oauth_effective_user => 'admin', websockets_encrypt => true, websockets_ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', websockets_ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/foreman01.pizza.local.pem', cors_domains => [], trusted_proxies => ['127.0.0.1/8', '::1'], } } |
Sull’host foreman01.pizza.local eseguire i comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
apt install ruby-foreman-puppet ruby-puppetdb-foreman -y groupadd puppet /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet resource service puppet ensure=running enable=true /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent -t |
A questo punto Foreman dovrebbe essere disponibile all’indirizzo: https://foreman.pizza.local
Accedere con le credenziali impostate tramite i parametri initial_admin_username e initial_admin_password.
Andare su Administer > Settings > General e configurare Foreman URL: https://foreman.pizza.local
INSTALLAZIONE DELLO SMART PROXY PER PUPPET
Sull’host 01.puppet.pizza.local eseguire i comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
touch /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/autosign.conf chown puppet:puppet /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/autosign.conf chmod 664 /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/autosign.conf /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet module install theforeman-foreman_proxy --version 25.1.0 |
Aggiungere le repository di Foreman con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
wget https://deb.theforeman.org/foreman.asc -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/foreman.asc echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ bullseye 3.5" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list echo "deb http://deb.theforeman.org/ plugins 3.5" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/foreman.list apt update |
Aggiungere nel file /etc/puppetlabs/puppetserver/conf.d/auth.conf il seguente output:
ATTENZIONE: La rule relativa a /puppet/v3/environments, dovrebbe già essere presente, aggiungere le altre due sotto di essa
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
{ match-request: { path: "/puppet/v3/environments" type: path method: get } allow: "*" sort-order: 500 name: "puppetlabs environments" }, { match-request: { path: "/puppet/v3/environment_classes" type: path method: get } allow: "*" sort-order: 500 name: "puppetlabs environment classes" }, { match-request: { path: "/puppet/v3/resource_type" type: path method: [get, post] } allow: "*" sort-order: 500 name: "puppetlabs resource type" }, |
Aggiungere nel file /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/foreman.yaml il seguente output:
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
--- :url: "https://foreman.pizza.local" :ssl_ca: "/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem" :ssl_cert: "/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem" :ssl_key: "/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem" :puppetdir: "/opt/puppetlabs/server/data/puppetserver" :puppetuser: "puppet" :facts: true :fact_extension: "json" :timeout: 60 :report_timeout: 60 :report_retry_limit: 1 :threads: null |
Aggiugere i file necessari a Puppet per ricevere da Foreman i parametri della ENC ed inviargli i reports con i seguenti comandi:
|
0 1 2 3 |
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/theforeman/puppet-puppetserver_foreman/master/files/report.rb -o /opt/puppetlabs/puppet/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/puppet/reports/foreman.rb curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/theforeman/puppet-puppetserver_foreman/master/files/enc.rb -o /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb chown puppet:puppet /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb chmod 550 /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb |
Aggiungere nel file /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf il seguente output:
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
[main] ... reports = log, foreman ... [master] ... external_nodes = /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/node.rb node_terminus = exec |
Riavviare il server con il comando:
|
0 |
systemctl restart puppetserver.service |
Aggiungere al file /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/manifests/01.puppet.pizza.it.pp il seguente output:
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
node '01.puppet.pizza.it' { # # ... # # Here we install and configure Foreman Proxy class { 'foreman_proxy': bind_host => ['0.0.0.0'], http => false, ssl => true, ssl_port => 8443, groups => ['puppet'], log => '/var/log/foreman-proxy/proxy.log', log_level => 'INFO', ssl_ca => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', foreman_ssl_ca => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', foreman_ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', foreman_ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', ssl_disabled_ciphers => [], tls_disabled_versions => ['1.1'], trusted_hosts => ['foreman01.pizza.local'], puppetca => true, puppetca_listen_on => 'https', ssldir => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl', puppetdir => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet', puppet_group => 'puppet', autosignfile => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/autosign.conf', manage_puppet_group => true, puppet => true, puppet_listen_on => 'https', puppet_url => 'https://puppet.pizza.it:8140', puppet_ssl_ca => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem', puppet_ssl_cert => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', puppet_ssl_key => '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/01.puppet.pizza.it.pem', templates => false, registration => false, logs => true, tftp => false, dhcp => false, dns => false, bmc => false, realm => false, register_in_foreman => true, registered_name => '01.puppet.pizza.it', registered_proxy_url => 'https://01.puppet.pizza.it:8443', foreman_base_url => 'https://foreman.pizza.local', oauth_effective_user => 'admin', oauth_consumer_key => '<oauth_random_string>', oauth_consumer_secret => '<oauth_longer_random_string>', } } |
Sull’host puppet01.pizza.local eseguire il comando:
|
0 |
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent -t |
CONFIGURAZIONE DI FOREMAN TRAMITE WEB GUI
Sulla web UI di Foreman andare su
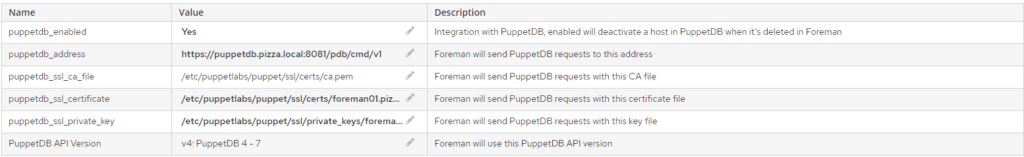
Selezionare dal menù Administer > Settings > PuppetDB
Quindi configurare le impostazioni mostrate nell’immagine sovrastante
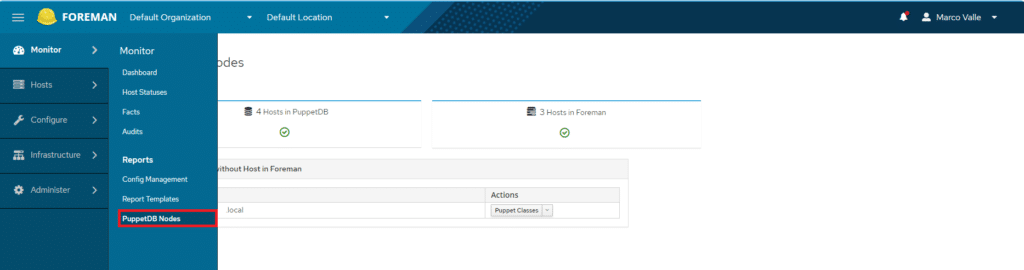
Andare su Monitor > PuppetDB Nodes
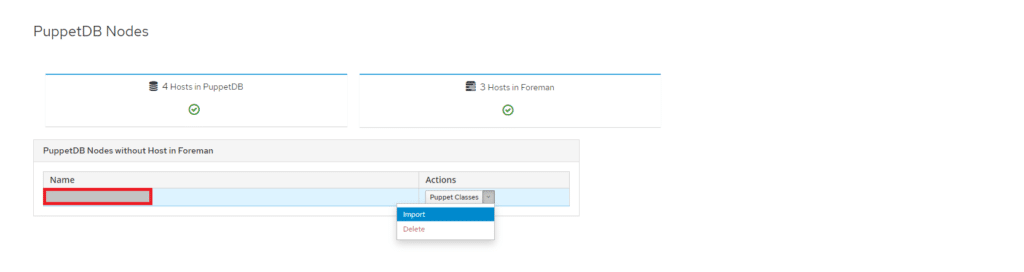
Quindi importare gli Host mancanti selezionando Actions quindi Import
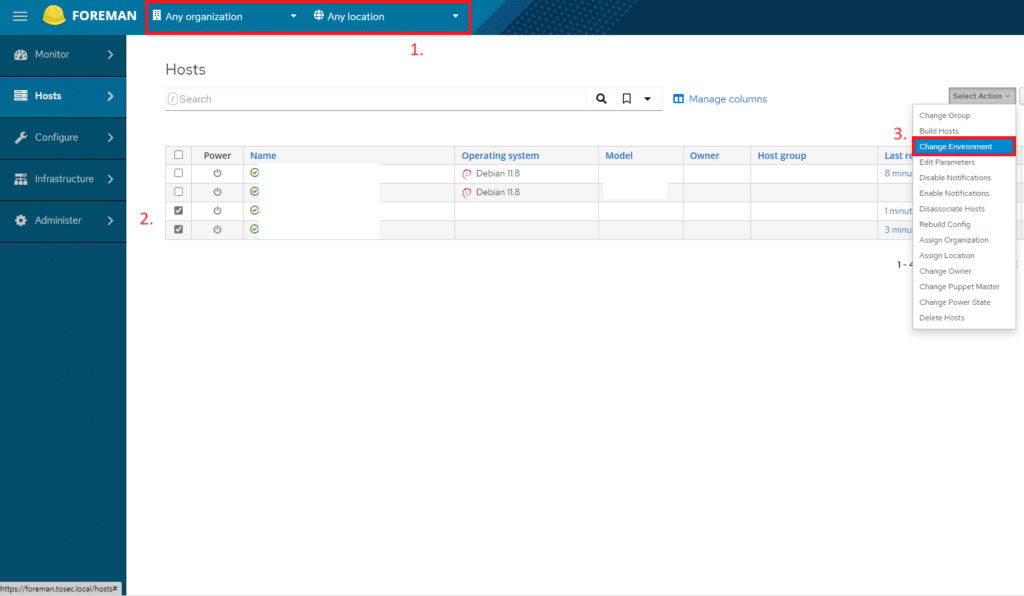
Andare su Hosts > All Hosts
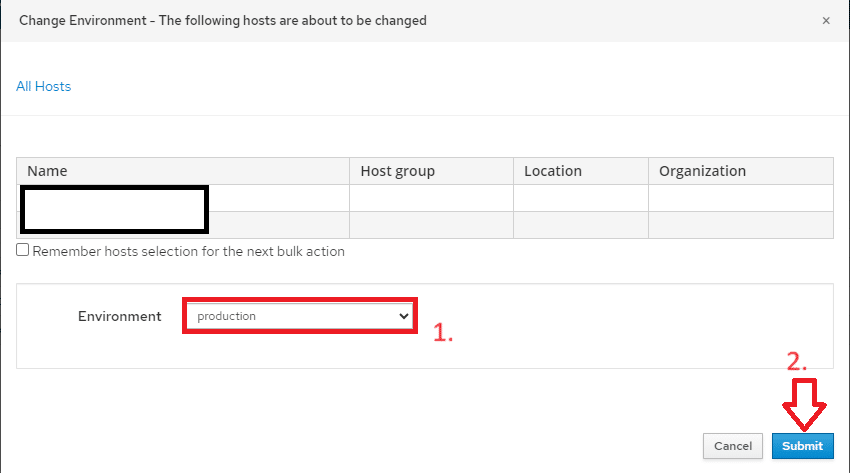
Impostare gli environments dei nodi importati come mostrato nell’immagine sovrastante
Quindi modificare l’environment e cliccare su Submit
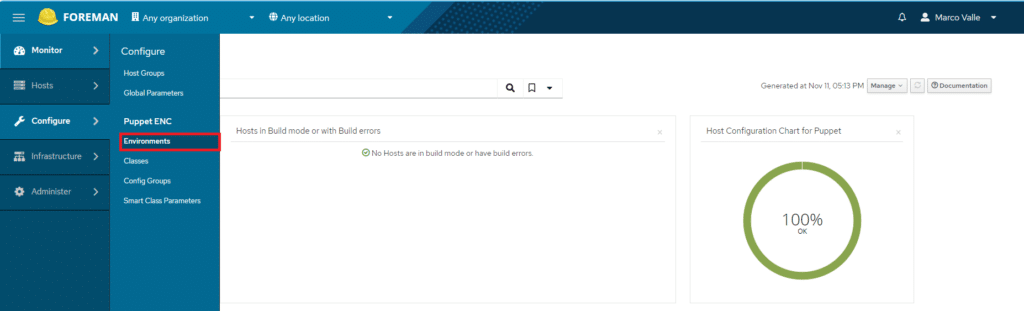
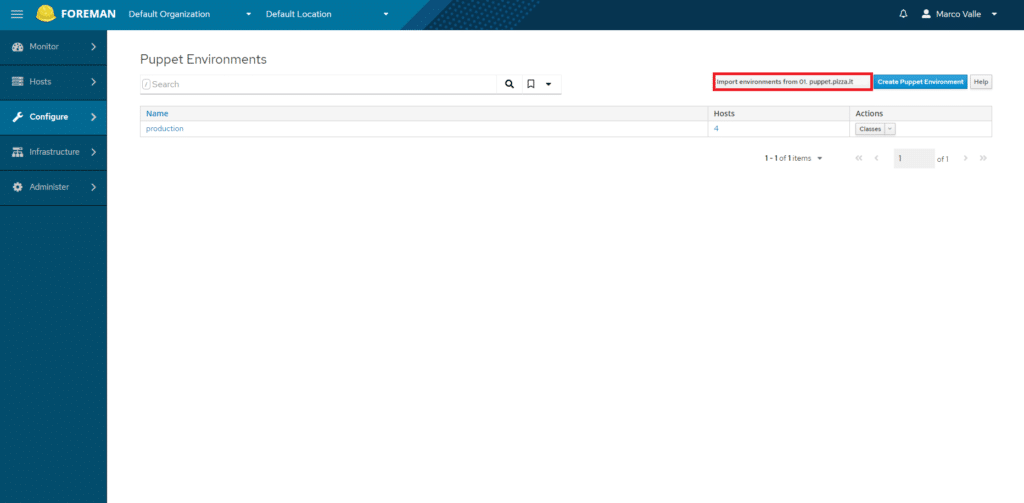
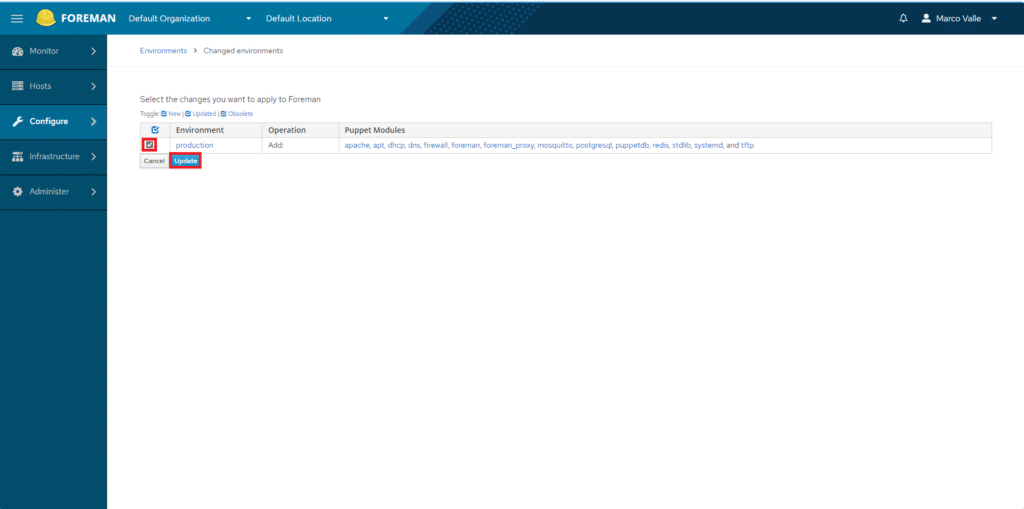
Andare su Configure > Enviroments
Quindi importare le classi di Puppet cliccando Import Environments from 01.puppet.pizza.local
A questo punto Foreman è pronto per essere utilizzato come Puppet ENC, ricevere i reports e consultare i facts.















![Errore in LibreNMS: Python3 module issue found: ‘Required packages: [‘PyMySQL!=1.0.0’, ‘python-dotenv’, ‘redis>=4.0’, ‘setuptools’, ‘psutil>=5.6.0’, ‘command_runner>=1.3.0’]](https://www.raffaelechiatto.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Errore_in_LibreNMS_Python3_module_issue_found-1080x675.png)













0 commenti